Receiving webhooks
Webhooks are delivered using an HTTP Post request to a specified URL. The system will not follow any redirects. A delivery is considered successful if an HTTP status code in the 200-299 range is received. Any response body is not interpreted by the system except for debugging purposes. If a status code outside the 200-299 range is received, the delivery is considered a failure and will be retried. The same applies for connection issues like timeouts or unresolvable DNS names. The delivery will be retried up to an implementation defined maximum with exponential backoff. If the amount of retries is exhausted, the event will no longer be delivered to that webhook. After too many such failures, the webhook will be automatically deactivated.
Robustness
Webhook delivery is designed to be robust. The system will attempt to retry deliveries, if no success status was received.
In rare circumstances a request might arrive in the target system and be processed, but the response fails to arrive,
for example due to network failure. In such a case your system might receive the same event twice, because the IoT Cloud
will attempt a re-delivery.
Use the eventId property to detect if an event has already been processed by your system.
Debugging
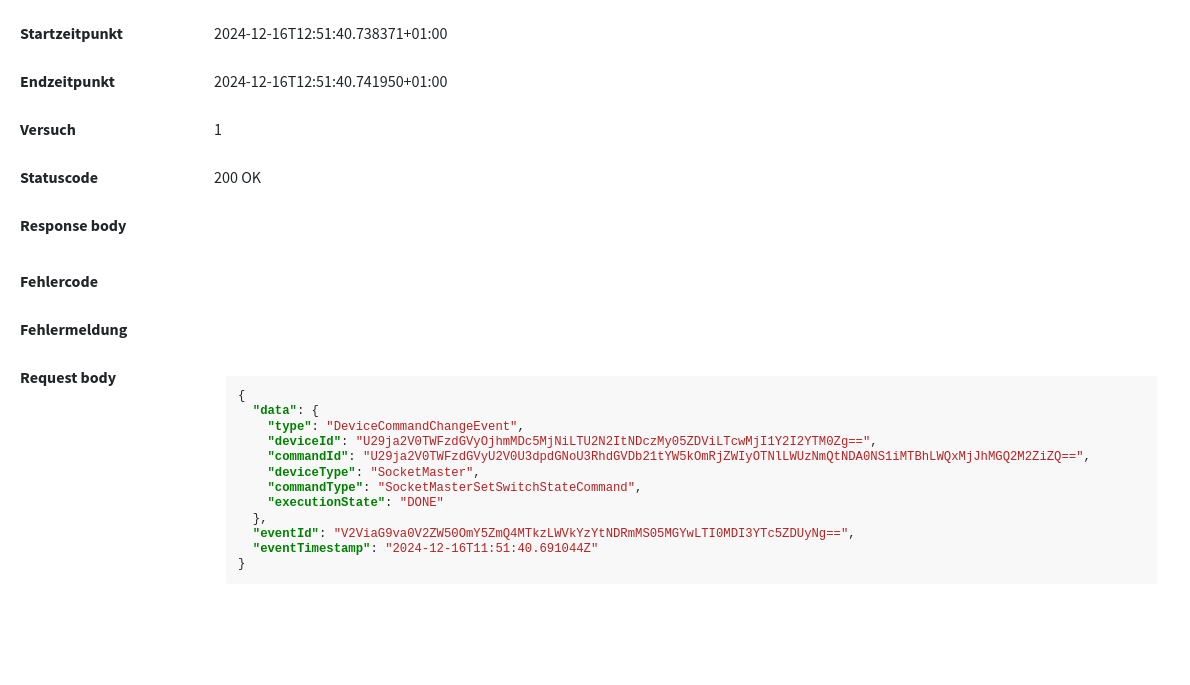
You can see the most recent attempted deliveries to your webhooks in the admin interface.
Reactivating a webhook
If a webhook fails repeatedly, it will be automatically disabled. The user who created the Webhook will be notified via email. To reactivate the webhook, simply reactivate it via the Admin interface or the GraphQL API.
Security
When a webhook is received, you should ensure it is authentic using the included HMAC. This ensures that the message originates from the Cynox IoT Cloud, because it has been cryptographically signed using the secret key configured on the webhook. Additionally, it prevents replay attacks by including the timestamp of the request in the hash.
See the following example code for how to accomplish this.
Using Express
5 collapsed lines
import express from 'express';import crypto from 'node:crypto';
const app = express();
app.use('/webhook', express.json({ verify(req, res, buf, encoding) { const incomingHmac = req.headers['x-cynox-webhook-hmac']; const incomingTsHeader = req.headers['x-cynox-webhook-timestamp']; if (!incomingHmac || !incomingTsHeader) { throw new Error('Missing headers'); } const incomingTs = Date.parse(incomingTsHeader); const myHmac = crypto.createHmac('sha256', 'your-secret-key') .update(incomingTsHeader) .update(buf) .digest(); if (!crypto.timingSafeEqual(myHmac, Buffer.from(incomingHmac, 'hex'))) { throw new Error('Invalid HMAC'); } const delta = incomingTs - Date.now(); if (Math.abs(delta) > 5000) { throw new Error('Outdated message'); } }}));
app.post('/webhook', (req, res) => { console.log('Webhook received', req.body); res.status(204).send();});2 collapsed lines
app.listen(3000);Using Django
16 collapsed lines
import datetimeimport hashlibimport hmacimport jsonimport loggingfrom hmac import compare_digest
from django.http import HttpRequest, HttpResponse, JsonResponsefrom django.utils import timezonefrom django.views import View
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class WebhookView(View): def post(self, request: HttpRequest) -> HttpResponse: raw_body = request.body data = json.loads(raw_body) incoming_hmac = request.headers.get('x-cynox-webhook-hmac') incoming_ts_header = request.headers.get('x-cynox-webhook-timestamp') if not incoming_hmac or not incoming_ts_header: return HttpResponse(status=400) incoming_ts = datetime.datetime.fromisoformat(incoming_ts_header) my_hmac = hmac.new('your-secret-key'.encode(), digestmod=hashlib.sha256) my_hmac.update(incoming_ts_header.encode()) my_hmac.update(raw_body)
if not compare_digest(my_hmac.digest(), bytes.fromhex(incoming_hmac)): return JsonResponse({'error': 'Invalid HMAC'}, status=400)
delta = incoming_ts.timestamp() - timezone.now().timestamp() if abs(delta) > 5: return JsonResponse({'error': 'Outdated message'}, status=400)
logger.info('Webhook received: %s', data) return HttpResponse(status=204)6 collapsed lines
<?phpif ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] !== 'POST') { http_response_code(405); exit;}
$content = file_get_contents('php://input');$incomingHmac = $_SERVER['HTTP_X_CYNOX_WEBHOOK_HMAC'];$incomingTsHeader = $_SERVER['HTTP_X_CYNOX_WEBHOOK_TIMESTAMP'];
if (empty($incomingHmac) || empty($incomingTsHeader)) { http_response_code(400); exit;}
$incomingTs = DateTimeImmutable::createFromFormat('Y-m-d\TH:i:s.uP', $incomingTsHeader);if ($incomingTs === false) { http_response_code(400); die(print_r(DateTimeImmutable::getLastErrors(), true));}
$myHmacCtx = hash_init('sha256', HASH_HMAC, 'your-secret-key');hash_update($myHmacCtx, $incomingTsHeader);hash_update($myHmacCtx, $content);$myHmac = hash_final($myHmacCtx, true);
if (!hash_equals($myHmac, hex2bin($incomingHmac))) { http_response_code(400); die('Invalid HMAC');}
$delta = $incomingTs->getTimestamp() - time();if (abs($delta) > 5) { http_response_code(400); die('Outdated message');}
$data = json_decode($content, true);
error_log('Webhook received: ' . print_r($data, true));